Code Signing Certificate vs. Email Signing & Document Signing Certificate
Find Out the Differences Between a Code Signing Certificate vs. an Email Signing or Document Signing Certificate
As a software developer, you certainly know how important code signing certificates are. But, many times, especially those who are new into the industry often have questions about how these code signing certificates differ from other certificates. For example, the difference between a Code Signing Certificate and SSL Certificate, or the difference between a code signing certificate and document signing certificate. One of the questions asked on largest and most trusted online communities: Stack Overflow, which intrigued to write about the difference between these two code signing certificates and document signing certificate.
However, please do note that both document signing certificates and email signing certificates are covered together. We didn’t compare these two separately with code signing certificates, because they’re basically the same thing—email signing and document signing often use the same type of certificate.
So, let’s get started.
First, let’s try to understand what each of them are and if there’s any similarity, then we’ll dig into the differences between the two.
What’s a Code Signing Certificate?
This whole website is exclusively dedicated to code signing certificates. So, I won’t go into much detail. Let’s put it this way: a code signing certificate is like a guarantee that the piece of code, application, executable file, or software has not been tampered with since it was signed by the software publisher.
You can also say a code signing certificate is similar to a wax seal that lets the recipient identify the author while confirming that the software hasn’t been opened or tampered with since the time it was signed. In other words, a code signing certificate issued by trusted certificate authority like Sectigo validates that if you, as a user, trust the software organization, then you can also trust their code.
Operating systems like Microsoft Windows take this very seriously. If anyone tries to install unsigned software on Windows, the user will be greeted with a warning sign like this:
On the other hand, if it’s signed especially using a Code Signing Certificate, then it’ll instantly bypass this Unknown Publisher warning message.
In some cases, unknown software may trigger a Microsoft SmartScreen security alert, like this:

In those cases, the software publisher can use an EV code signing certificate to verify their identity so users won’t see the popup.
What’s an Email Signing or Document Signing Certificate?
As the name implies, email signing and document signing certificates are those which are used for digitally signing emails and documents. They enable organizations to digitally sign emails and different document types like Microsoft Office and Adobe while marking them with visual trust indicators. The certificate shows the identity of the sender while indicating the document or email came from the expected source and has not been altered.
In other words, it helps you avoid spoofed business emails and email compromises, signs essential documents and files, and ensures document integrity.
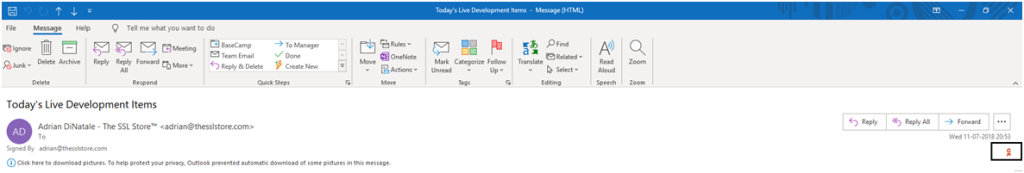
Email signed using Email Signing Certificate
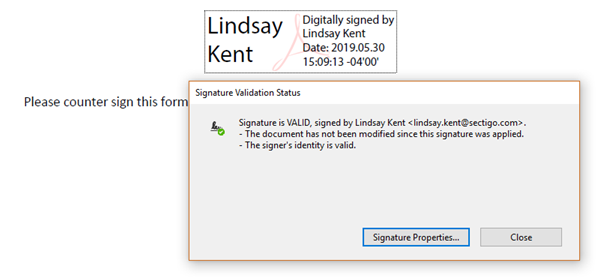
Document Signed Using Document Signing Certificate
Similar to other X.509 certificates, it provides visual trust indicators to the recipient that the sender’s identity is verified, and the received document or email hasn’t been tampered with during transmission.
Similarities Between: Code Signing Certificate and Email Signing / Document Signing Certificate
At one level, you can say they’re are somewhat similar to each other, as they’re both used for proving that the data (software package, email or documents) is coming from the intended party, and it hasn’t been tampered with. A few of the similarities are:
- Code signing certificates and email signing/document signing certificates are all digital certificates, which belong to the x.509 family and use PKI (Public Key Infrastructure).
- Before issuance, the certificate’s applicant has to go through a rigorous vetting process from the certificate authority.
- They’re all used to protect users from becoming victims to cybercrime.
- They both provide a validity period of one year, two years, and three years.
Differences Between a Code Signing Certificate and an Email & Document Signing Certificate
| Code Signing Certificate | Email & Document Signing Certificate | |
|---|---|---|
| Secures |
It secures:
|
It secures:
|
| Users | Software publishers or developers. |
|
| Validation |
Two types of validation are offered:
|
Three types of validation are offered:
|
| Number of Signings | Unlimited | Varies depending upon type, whether it’s Individual or Organization, and also the certificate authority. For example, DigiCert lets you sign anywhere from 500 to 5000, depending upon the certificate you choose. |
| After Certificate Expiry | Once the validity period of a code signing certificate expires, you won’t be able to sign new software and executable files. Though, past signatures will remain valid and won’t display any warning message, only if it was time-stamped at the time of signing. | A signature will remain valid, but you won’t be able to sign new documents and emails using that expired certificate. |
| Assurance | Give assurance to users that they can trust the software and other executable files. | Give assurance to users that the document or mail they’re reading has come from the expected source. |
| Certificate Authorities | Thawte, Symantec, Comodo/Sectigo |
Comodo offers a certificate called CPAC (Comodo Personal Authentication Certificates), which is a combination of both: Email Signing Certificate as well as Document Signing Certificate. Document and email signing certificates are offered separately by CAs such as DigiCert. |
| Read More |
Closing Thoughts
To sum up, in today’s date, most work and communication is done with software as well as emails and documents. That’s why it’s crucial to use a valid digital signature, so users can be assured that the software they’re downloading or document or email they’re reading is coming from a trusted source.
Code signing and email/document signing certificates do differ from each other. But they’re similar in some ways: these certificates are essential and work towards one goal of providing security to the users while preventing any unwanted security threat.