How to View Certificates on Windows 10 (Using Windows 10 Certificate Manager)
This brief guide introduces you to Windows 10 Certificate Manager. This tool allows you to view and manage installed digital certificates on Windows devices as well as view CRLs and CTLs as well
When you install digital certificates onto your computer, there’s one place where they should be imported right away: the Windows 10 Certificate Manager. This tool is an easy-to-use console where you can view installed certificates on your Windows 10 device all in one place. This includes:
- Code signing certificates
- Client authentication certificates
- Document signing certificates.
But the Windows 10 Certificate Manager doesn’t store only your personal or organizational certificates — it’s also where you can view:
- All publicly trusted root certificates that are pre-installed on your device,
- Certificate revocation lists (CRLs), and
- Certificate trust lists (CTLs).
This article will familiarize you with the Windows 10 Certificate Manager tool that’s built into your machine. After that, we’ll walk you through the processes of how to view both organizational and publicly trusted digital certificates that are installed on your device.
What Is the Windows 10 Certificate Manager? It’s How You Can View Installed Certificates
The Certificate Manager is a console that comes installed on every modern Windows computer. It’s a tool that enables you to do many things relating to digital certificates that are installed on your device, including:
- View installed certificates,
- Modify your certificates,
- Export existing certificates,
- Delete existing certificates, and
- Import new certificates.
This is also where you can view your device’s trust store for publicly trusted certificates (i.e., certificates issued by trusted certificate authorities [CAs]) that come pre-installed on your device. More on that toward the end of the article. But first, there’s one other important thing to mention before we move on to how to view certificates in Windows 10.
There are Two Types of Window Certificate Manager Tools (Snap-In vs Command-Line Utility)
Certmgr.msc is a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in. The snap-in is a handy interface where you can add specific tools to your device’s admin console (e.g., a certificate manager). This differs from the Certmgr.exe, which is a command-line utility certificate manager.
Now that we know what Windows Certificate Manager console is and why it’s useful, let’s get right to how you can use it to view, delete or install certificates onto your device.
How to View Installed Certificates on Windows 10 (Organizational & Individual Certificates)
1. First, open your Windows 10 Certificate Manager. You can do this by typing either Cert or Certificate in the run menu.
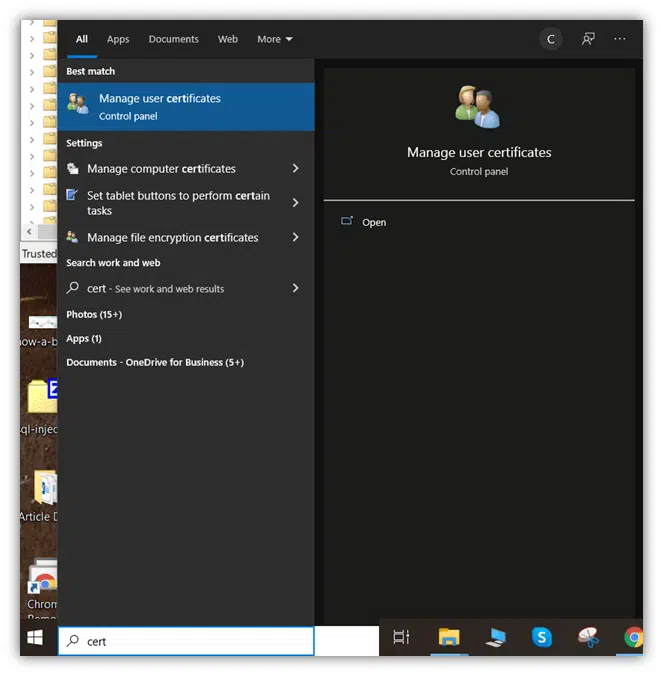
2. Select the Manage user certificates option at the top of the menu. This will populate another window title Certmgr. This is the Certificate Manager tool, which allows you to view installed certificates on Windows 10.
3. In the left pane, double-click the Personal folder to display a sub-folder titled Certificates.
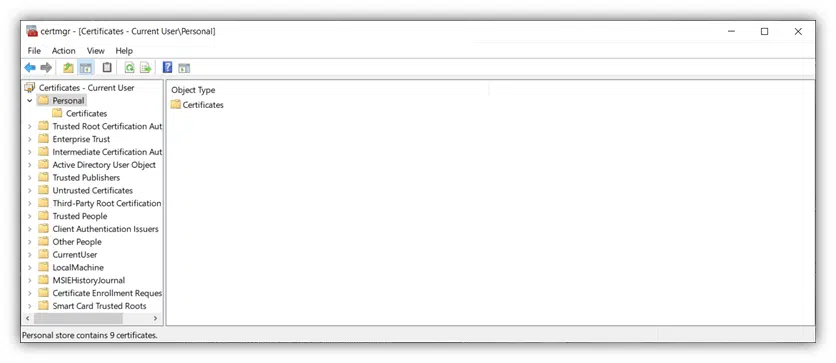
4. Select the Certificates folder in the left navigation to view the list of digital certificates you have installed on your machine. These will display in the right pane.
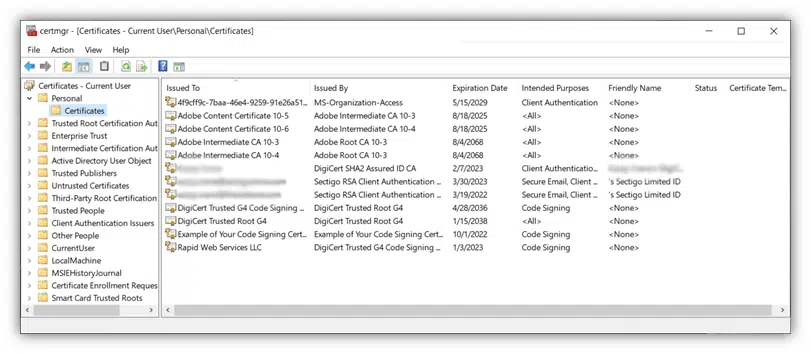
That’s it! Now, you can view any of these individual certificates by simply double-clicking on it. Doing this will open a new window that displays the digital certificate’s information, including:
- The certificate’s intended uses,
- Who it’s assigned to, and
- What trusted certificates it stems from and whether it’s trustworthy.
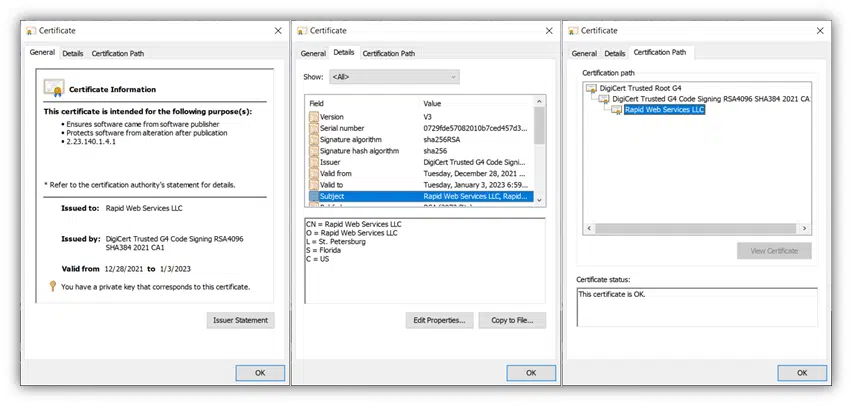
Now you know how to view installed certificates on Windows 10! Of course, if you’re curious to know what certificates you have installed on your device through Windows, then keep reading.
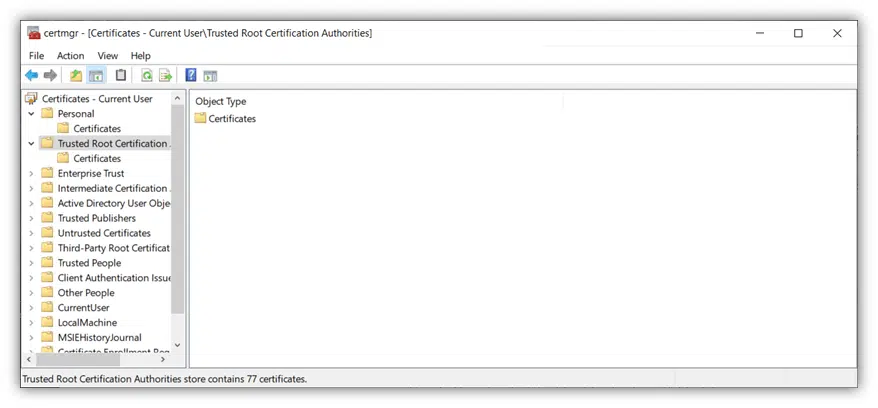
This will display a folder labeled Certificates, which will display the trusted root certificates that are installed on your device:
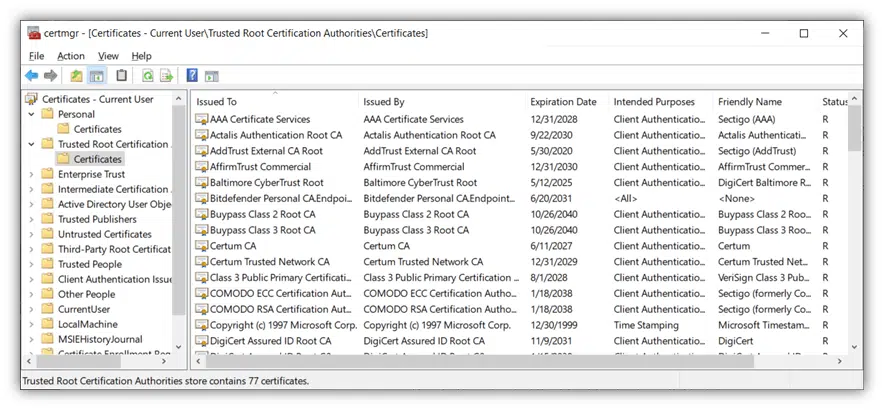
That’s it! As you can see, understanding how to view certificates on Windows 10 isn’t complicated at all once you know what it is you’re looking for. There’s really nothing to it.
If you want to learn how to import or install a code signing certificate on Windows, check out our other guide.